The Function and Manufacturing Process of Ship Main Engine Parts
Ship Main Engine Parts: Functions, System And Manufacturing
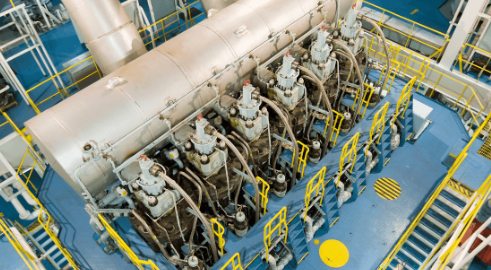
The sturdy foundation of a ship’s main engine, housing cylinders and critical components.
Ships rely on a crucial part of their journey across vast oceans—the main engine. This powerful component of maritime transport has a long history, evolving from early steam engines to today’s advanced marine diesel engines. A marvel of engineering, the ship’s main engine is the heart of its propulsion system, moving vessels of immense size through the turbulent waves.
A ship’s main engine is a complex assembly of various essential parts and systems, each with a specific function contributing to the propulsion mechanism. From the sturdy pistons to the intricate fuel injection systems, every component works harmoniously to convert fuel into energy. The crankshaft, for instance, transforms the up-and-down motion of the pistons into a rotary motion, driving the propeller and propelling the ship forward.
This article aims to dissect these components and understand the ship’s main engine, functions, intricate systems, and the meticulous manufacturing processes that bring this engineering marvel to life.
What are Ship Engine Parts?
A ship’s engine, or the main engine or propulsion system, is the primary mechanical system that makes the boat move through water. It’s like the ship’s heart, providing the power to drive the propeller and push the vessel forward.
A ship’s main engine part converts fuel into the mechanical energy needed to propel the vessel through water. This intricate machinery is composed of various essential parts, each playing a crucial role in the overall functioning of the engine. These parts include pistons, crankshafts, fuel injection systems, cooling systems, lubrication systems, exhaust systems, turbochargers, camshafts, connecting rods, and cylinder liners.
Components of The Ship’s Main Engine Parts
Precision-engineered components deliver fuel to the engine’s combustion chamber.
The components of a ship’s main engine are meticulously designed and manufactured to ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and reliability. They are manufactured using advanced techniques like CNC machining, which brands like Zintilon, Wayken, and Rapid Direct are experts in. Here are the components and how they play a crucial role in ships’ safe and successful navigation worldwide.
Engine Body
The engine body, also known as the engine block or cylinder block, forms the structural foundation of the ship’s main engine. Constructed from durable materials like cast iron or aluminum alloy, the engine body is designed to withstand the immense forces and pressures generated during the engine’s operation.
Function:
- Support and Alignment: The engine body provides a rigid framework for supporting and aligning the cylinders, pistons, and crankshaft.
- Heat Dissipation: It also serves as a heat sink, absorbing and dissipating the heat generated by combustion.
- Stability and Durability: The sturdy construction of the engine body ensures the longevity and reliability of the entire engine system.
Manufacturing Technique:
- Casting: The engine body is often created through casting, where molten metal is poured into a mold to form the desired shape. This ensures the formation of a solid and robust structure.
- Machining: After casting, the engine body undergoes precision machining processes such as milling, drilling, and grinding to achieve precise dimensions and smooth surfaces. For your machining needs, you can contact brands like Rapid Direct, Wayken, and Zintilon.
Fuel Supply System
The fuel supply system of a ship’s main engine is responsible for delivering the precise amount of fuel to the combustion chamber for efficient combustion. It plays a crucial role in optimizing fuel consumption and engine performance.
Function:
- Fuel Delivery: The system delivers fuel to the engine cylinders at the correct pressure and timing for optimal combustion.
- Fuel Atomization: It ensures that the fuel is finely atomized or mixed with air to form an explosive mixture.
- Control and Regulation: The system controls the fuel flow rate and injection timing based on engine load and speed.
Manufacturing Technique:
- Fuel Injectors: These precision-engineered components are designed to deliver fuel in controlled sprays, ensuring efficient combustion.
- Fuel Lines and Pump: Constructed from materials like stainless steel or reinforced rubber, these components are manufactured precisely to handle high-pressure fuel delivery without leaks or failures.
Intake and Exhaust System

Intake and Exhaust System: Bringing in fresh air and removing burned gases from engine cylinders
The intake system brings in fresh air for combustion, while the exhaust system removes the burned gases from the engine cylinders. These systems are vital to the engine’s performance and emissions control.
Function – Intake System:
- Air Filtration: Filters out contaminants from the incoming air to protect the engine.
- Air Regulation: Regulates the airflow to maintain the optimal air-fuel ratio for combustion.
Exhaust System:
- Gas Removal: Removes the burned gases from the engine cylinders to maintain engine efficiency.
- Emissions Control: Reduces harmful emissions and pollutants before releasing them into the environment.
Manufacturing Technique:
- Intake Manifold and Air Filters: These components are precision-manufactured from lightweight yet durable materials like aluminum alloys. They are designed to optimize airflow and filtration efficiency.
- Exhaust Manifold and Pipes: Constructed from heat-resistant materials such as stainless steel, these components are designed to withstand high temperatures and corrosive exhaust gases without warping or deteriorating.
Cooling System
The cooling system of a ship’s main engine is essential for regulating its operating temperature and preventing overheating. It ensures the engine operates within the optimal temperature range for efficiency and longevity.
Function:
- Heat Dissipation: Absorbs and dissipates the heat the engine generates.
- Temperature Regulation: Maintains the engine at a consistent temperature to prevent overheating.
- Component Protection: Protects engine components from damage due to excessive heat.
Manufacturing Technique:
- Radiators: Engineered from materials such as aluminum, radiators are precision-manufactured to maximize heat dissipation and cooling efficiency.
- Coolant Hoses and Pump: These components are constructed from flexible yet durable materials and are designed to withstand the high temperatures and pressures of the cooling system.
Lubrication System
The lubrication system ensures the smooth operation of the engine’s moving parts by reducing friction and wear. It provides a protective layer of oil to critical components such as pistons, crankshafts, and bearings.
Function:
- Friction Reduction: Reduces friction between metal surfaces to prevent wear and prolong component life.
- Heat Dissipation: Absorbs and carries away heat generated by friction.
- Corrosion Protection: Protects metal surfaces from corrosion and oxidation.
Manufacturing Technique:
- Oil Pump and Pan: Precision-engineered components that deliver oil to critical engine parts. These are designed to ensure proper oil flow and lubrication under varying operating conditions.
- Oil Filters are precision-manufactured to remove contaminants and effectively maintain oil cleanliness. They play a vital role in ensuring the longevity of the engine’s components.
Control System
The control system of a ship’s main engine manages and regulates its operation, ensuring optimal performance, fuel efficiency, and reliability. It monitors various engine parameters and adjusts fuel delivery, timing, and functions accordingly.
Function:
- Parameter Monitoring: Monitors engine speed, temperature, pressure, and other vital parameters.
- Fuel Regulation: Adjusts fuel injection timing and amount based on engine load and speed.
- Engine Safety: Ensures safe engine operation by detecting and responding to abnormal conditions.
Manufacturing Technique:
- Electronic Control Units (ECUs): These sophisticated electronic components process data from sensors and control the engine’s operation. ECUs are precision-manufactured to provide precise control over engine parameters.
- Sensors: These precision-engineered components measure various engine parameters such as temperature, pressure, and speed. They provide real-time data to the control system for accurate adjustments.
Start System
The start system initiates the engine’s operation by providing the necessary energy to start the combustion process. It includes components such as the starter motor and ignition system.
Function:
- Crankshaft Rotation: Engages the starter motor to turn the crankshaft and operate the engine.
- Ignition: Provides electrical power to the ignition system, which sparks the fuel-air mixture for combustion.
- Preheating (In Some Systems): Preheats the engine components for easier starting in cold conditions.
Manufacturing Technique:
- Starter Motor: A precision-engineered component designed for high torque and reliability. It is manufactured to withstand the demands of starting a large marine engine.
- Ignition System Components: These include spark plugs and ignition coils, which are manufactured with precision to ensure reliable ignition and combustion.
Auxiliary System
A ship’s main engine’s auxiliary system includes various components supporting its operation and the vessel’s overall functions. This system provides power for ship systems, air for various ship functions, and hydraulic power for steering and other operations.
Function:
- Power Generation: Provides electrical power for ship systems, lighting, and equipment.
- Air Supply: Supplies compressed air for pneumatic systems, air brakes, and other ship functions.
- Hydraulic Power: Supports hydraulic systems for steering, winches, and other mechanical operations.
Manufacturing Technique:
- Power Generation Components: Alternators or generators are precision-engineered for efficient and reliable power generation. They are manufactured with high-quality materials for durability.
- Air Compressors: These components are designed to deliver compressed air efficiently and reliably. They are manufactured with precision to withstand the demands of ship operations.
- Hydraulic Components: Precision manufacturing techniques create hydraulic pumps, valves, and actuators, which are designed to provide precise and reliable operation for ship systems.
Here’s a table summarizing the benefits of a ship’s main engine:
| Benefits | Description |
| Efficient Propulsion | Converts stored energy in fuel to mechanical force, propelling ships forward efficiently through the water. |
| Reliable Performance | It ensures consistent and dependable operation, which is vital for long journeys across the seas. |
| Fuel Efficiency | Optimizes fuel consumption, reducing costs and environmental impact. |
| Longevity and Durability | Designed with durable materials and advanced manufacturing techniques for extended service life. |
Conclusion
The ship’s main engine is a prime example of smart precision engineering. It is the main power moving ships across the big oceans. Every part has an important job, which is to make the engine work smoothly. These parts are made with special techniques such as 5 axis CNC machining and tough materials to ensure efficient, reliable, and safe voyages at sea. Consider regular maintenance checks and updates to ensure your ship’s main engine continues to operate at its best.
Stay in touch to get more updates & news on Discover Headline!