The Importance and Impact of Energy Storage Systems on Future Energy Management
Introduction to Energy Storage Systems
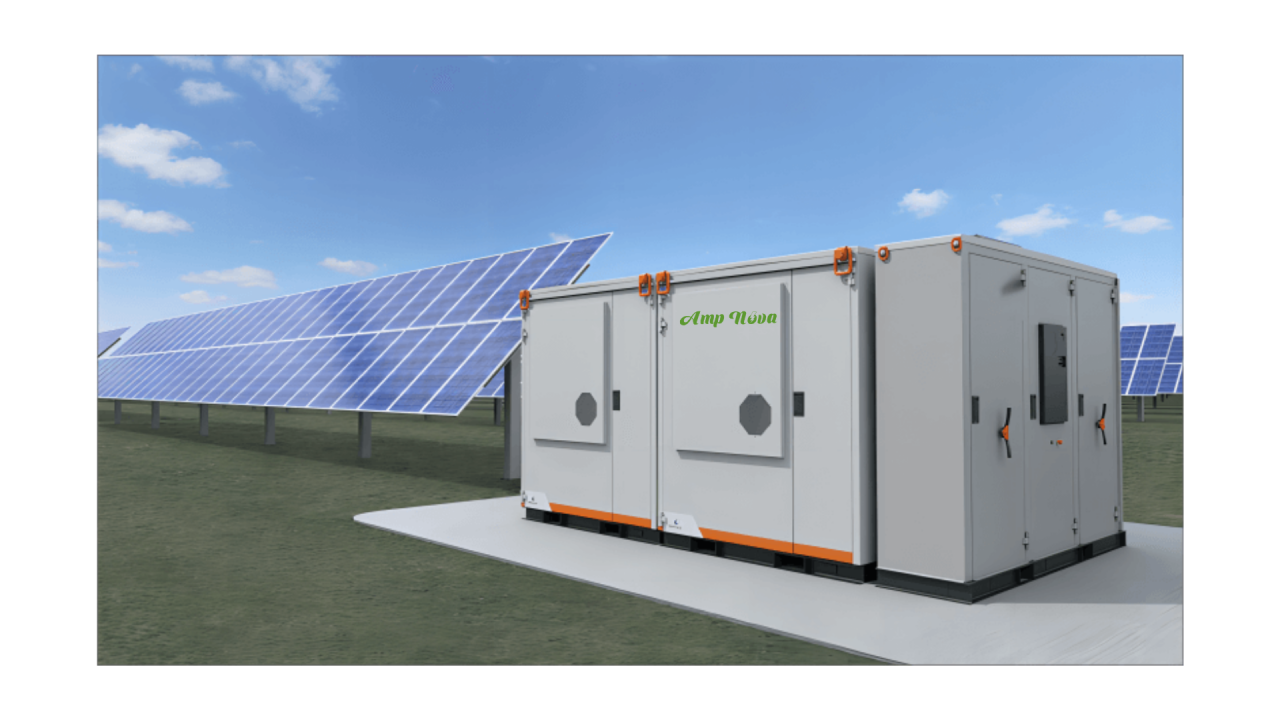
The transformation of the energy landscape is palpable in the rise of Energy Storage Systems (ESS), a linchpin in the modernization of power grids. As the shift toward renewable energy gains momentum, ESS is indispensable, balancing supply and demand, mitigating the impacts of power fluctuations, and acting as a cornerstone for the next generation of power management solutions. Storage systems bridge the gap between the availability of naturally intermittent renewable energy sources and our constant energy demands, ultimately promoting sustainability and resilience within the power sector.
Types of Energy Storage Systems
Energy storage is an umbrella term for various technologies with distinct advantages and ideal uses. Mechanical storage methods, such as pumped-storage hydroelectric systems, are well-known for their large-scale energy management capabilities. In contrast, batteries, representing chemical storage, shine in their versatility and fast response times. Thermal energy storage effectively captures and stores heat, which can be used for heating or power generation later on. In contrast, electrical storage options like flywheels and supercapacitors excel in their ability to deliver quick bursts of power, effectively stabilizing the electricity supply. Understanding the complex technologies that comprise ESS is essential for appreciating their role in an evolving energy economy.
The Function of Energy Storage in Renewable Integration
To achieve a sustainable energy future, it’s crucial to successfully integrate renewable sources like wind and solar into the power grid. This is where ESS plays a transformational role. By storing energy when production exceeds demand and releasing it during shortages, storage systems can smooth out the unpredictability of renewable power generation. This balancing act is not just theoretical; it’s a practical necessity for maintaining the reliability of power systems as we increasingly turn to renewable energy.
Enhancing Grid Stability and Reliability
One of the cornerstone benefits of ESS is its contribution to grid stability. As the energy mix becomes more diversified with the inclusion of renewable energy sources, maintaining a stable power supply becomes more complex. Energy storage systems provide a crucial service by absorbing excess electricity and releasing it as needed, acting as a buffer against power disruptions. This capability is pivotal for industrial applications and critical infrastructure like hospitals and emergency services, ensuring that the lights stay on and machinery operates without interruption.
Energy Storage in Residential and Commercial Sectors
ESS is breaking ground beyond the confines of industrial applications and utility-scale projects. It’s reshaping the energy landscape at the grassroots level in both residential and commercial domains. Homeowners are using battery storage to harness solar power, reduce reliance on the grid, and protect against outages. At the same time, businesses leverage these systems for demand-side management and to stabilize operational costs. The decentralization of energy storage represents a democratic shift in energy resources, allowing individuals greater control over their energy usage and contributing to a more resilient grid ecosystem.
Financial Implications of Energy Storage Systems
The economics surrounding ESS is as dynamic as the technology itself. While costs have traditionally been a barrier to mass adoption, the landscape is changing rapidly. Economies of scale, technological innovations, and increased market demand are converging to make energy storage systems more affordable. As costs continue to fall, the long-term benefits, such as reduced energy bills, the possibility of energy arbitrage, and enhanced grid services, highlight the financial viability of ESS investments. This bodes well for energy consumers and a global economy increasingly focused on sustainable growth.
Policy and Regulatory Environment
The advancement of ESS is significantly influenced by the legislative framework set forth by governmental bodies. While market penetration may be slowed by a lack of supportive legislation, incentives like tax credits, rebates, and subsidies can increase adoption rates. Regulations that recognize and compensate for the myriad benefits of energy storage, from grid support to renewable integration, are vital. Policymakers are tasked with the challenge of keeping pace with technology developments while working to build a robust legal framework that facilitates sustainable energy innovation.
Innovations and Future Technologies in Energy Storage
New frontiers in ESS technology are consistently being explored, promising to reshape the efficiency and capability of these systems. Contemporary research is focused on extending the lifespan of batteries, increasing the energy density of storage mediums, and uncovering lower-cost materials. Progress in this field promises enhanced system performance and opens doors to novel energy storage applications in everyday life.
Case Study: Energy Storage Systems in Action
Case studies of ESS demonstrate their tangible impact when applied thoughtfully within communities and industries. Whether it’s a remote village achieving energy autonomy or a city using storage to buffer peak energy demands, these success stories attest to the transformative power of effective energy storage solutions. They exemplify how the strategic deployment of ESS can facilitate a shift towards a more sustainable and reliable energy future.
The Global Perspective on Energy Storage
On a global scale, the adoption of ESS varies widely and is impacted by regional policies, technological access, and economic factors. Some nations are in charge of implementing advanced storage solutions, while others are in the nascent stages of recognizing their benefits. Collaborative efforts across borders are vital for the widespread uptake and standardization of storage systems, facilitating a collective move towards an energy-resilient world. By sharing insights and learnings, the global community can accelerate the advancements and application of energy storage technologies.
The Path Forward: Integrating Storage Into Energy Planning
As we envisage the energy panorama of the future, incorporating ESS into holistic energy planning is non-negotiable. They are the building blocks of a flexible, responsive, and sustainable grid, enabling the alignment of energy production with consumption patterns. All stakeholders—regulators, energy providers, and end-users—must collaborate and innovate, ensuring ESS occupies its rightful place at the heart of energy solutions. Ultimately, integrating energy storage into our energy systems is a crucial step toward a cleaner, more sustainable, and resilient energy framework for future generations.
Stay in touch to get more updates & news on Discover Headline!